On this page:
Home > Beginners Guide to Aeronautics Propulsion System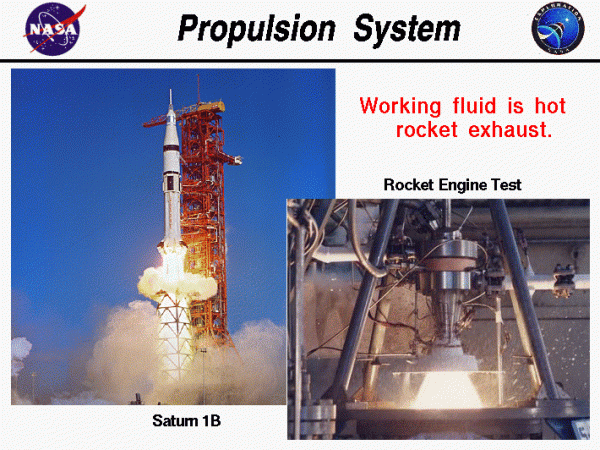 On this page, we show a picture of a Saturn 1B at the left and a picture of a rocket engine test at the right. For the picture at the right, we only see the outside of the rocket nozzle, with the hot gas exiting out the bottom. The first stage of the Saturn 1B was powered by eight liquid rocket engines burning a hydrocarbon fuel with liquid oxygen. The second stage used a single liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen powered engine and was used to place the Apollo spacecraft into low Earth orbit.
Propulsion System
On this page, we show a picture of a Saturn 1B at the left and a picture of a rocket engine test at the right. For the picture at the right, we only see the outside of the rocket nozzle, with the hot gas exiting out the bottom. The first stage of the Saturn 1B was powered by eight liquid rocket engines burning a hydrocarbon fuel with liquid oxygen. The second stage used a single liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen powered engine and was used to place the Apollo spacecraft into low Earth orbit.
Propulsion System
There are four major components to any full-scale rocket: the structural system, or frame, the payload system, the guidance system, and the propulsion system. The propulsion of a rocket includes all of the parts which make up the rocket engine, the tanks pumps, propellants, power head and rocket nozzle. The function of the propulsion system is to produce thrust.
Thrust is the聽force聽which moves a rocket through the air and through space. Thrust is generated by the聽propulsion system聽of the rocket. Different propulsion systems develop thrust in different ways, but all thrust is generated through some application of Newton’s聽third law聽of motion. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. In any propulsion system, a聽working fluid聽is accelerated by the system and the reaction to this acceleration produces a force on the system. A general derivation of the聽thrust equation聽shows that the amount of thrust generated depends on the聽mass flow聽through the engine and the聽exit velocity聽of the gas.
Rocket EngineIn a聽rocket聽engine,聽fuel and a source of oxygen, called an oxidizer, are mixed and exploded in a combustion chamber. The聽combustion聽produces hot exhaust which is passed through a聽nozzle聽to accelerate the flow and聽produce thrust. For a rocket, the accelerated gas, or聽working fluid,聽is the hot exhaust produced during combustion. This is a different working fluid than you find in a gas turbine engine or propeller powered aircraft. Turbine engines and propellers use air from the atmosphere as the working fluid, but rockets use the combustion exhaust gases. In outer space there is no atmosphere so turbines and propellers cannot work there. This explains why a rocket works in space but a turbine engine or a propeller does not work.
Liquid & Solid RocketsThere are two main categories of rocket engines: liquid rockets聽and聽solid rockets. In a聽liquid rocket,聽the聽propellants, the fuel and the oxidizer, are stored separately as liquids and are pumped into the combustion chamber of the nozzle where burning occurs. In a聽solid rocket,聽the propellants are mixed together and packed into a solid cylinder. Under normal temperature conditions, the propellants do not burn; but they will burn when exposed to a source of heat provided by an igniter. Once the burning starts, it proceeds until all the propellant is exhausted. With a liquid rocket, you can stop the thrust by turning off the flow of propellants; but with a solid rocket, you he to destroy the casing to stop the engine. Liquid rockets tend to be heier and more complex because of the pumps and storage tanks. The propellants are loaded into the rocket just before launch. A solid rocket is much easier to handle and can sit for years before firing.
