An ECG test, or electrocardiogram, is one of the most widely used tools in cardiac care, offering a fast and painless way to record a patient鈥檚 heart rhythm and electrical activity. For private clinics, it鈥檚 often the first test carried out when a patient presents with chest pain, dizziness, palpitations, or shortness of breath.
Quick to perform and rich in diagnostic value, the ECG test provides a visual trace of the heart鈥檚 rhythm, helping to identify issues such as arrhythmias, heart block, or signs of a previous heart attack. With accurate interpretation, clinics can make informed decisions faster, leading to better outcomes and greater patient confidence.
At Crane Cardiac Diagnostics, we support clinics by offering expert ECG analysis with fast turnaround times, enabling your team to stay focused on patient care while we handle the interpretation.
How Does an ECG Test Work?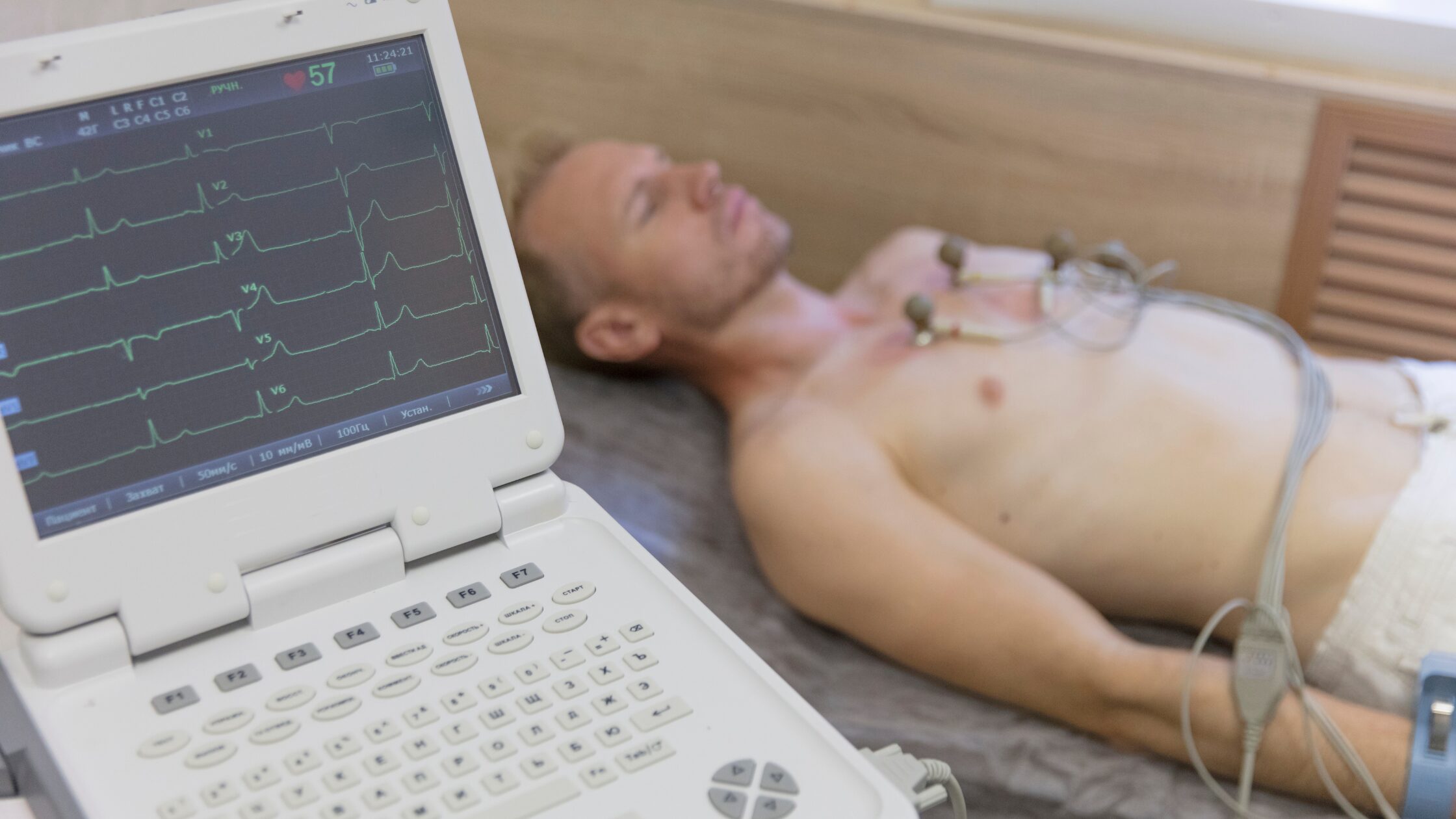
For private clinics, offering ECG testing is a quick and effective way to assess a patient鈥檚 cardiac function. The test itself takes less than 10 minutes and can be carried out during a routine appointment or as part of a more urgent assessment. Understanding what is an ECG test and how it works helps clinical staff explain the process clearly to patients while also knowing when to escalate or refer for further review.
During the ECG test, small sticky pads called electrodes are placed on the patient鈥檚 chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes pick up the electrical signals created by the heart as it beats. The signals are then displayed as a graph or series of lines on a screen or printout, showing the timing and strength of the heart’s activity.
The test is completely painless. The only discomfort might come from removing the electrodes after the test, especially if there is body hair, but this is minimal. Patients are asked to lie still and breathe normally, as movement can interfere with the recording. No electricity is sent into the body, it鈥檚 simply recording what the heart is already doing.
Once the data is recorded, it needs expert analysis to be truly valuable. That鈥檚 where Crane Cardiac Diagnostics supports clinics, by providing professional ECG interpretation, handled by experienced cardiac physiologists. Whether you’re using 12 lead ECGs or Holter monitors, we ensure fast and reliable reporting, so you can diagnose with confidence and speed.
For more on how ECG testing supports private healthcare, read our article on why ECG diagnostic services are essential for private clinics.
What Does an ECG Test Show?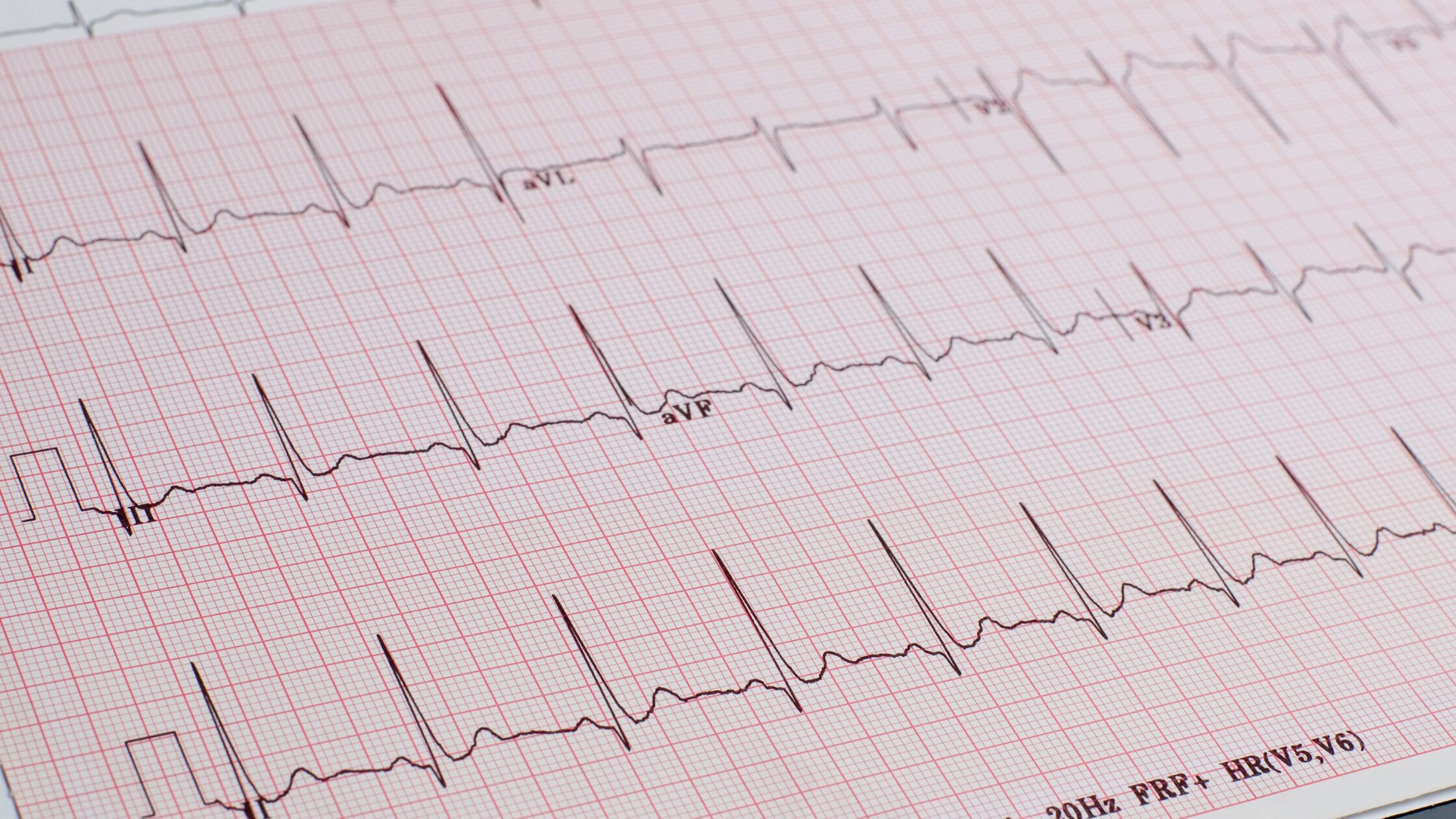
An ECG test provides a detailed look at how the heart is functioning in real time. While the test itself is quick and non invasive, the information it gives can be vital in spotting early signs of cardiac problems or confirming a diagnosis.
One of the main things an ECG looks at is heart rhythm, whether the heart is beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly. This can help detect conditions such as atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, or bradycardia. The ECG also shows the heart rate, allowing clinicians to see if it falls within a healthy range.
Beyond rhythm and rate, an ECG can show signs of a previous heart attack or ongoing restricted blood flow to the heart. This is seen through changes in the we patterns produced by the heart鈥檚 electrical activity. It may also highlight enlargement of the heart chambers, which can suggest conditions like high blood pressure or valve disease.
In some cases, ECGs are used to check how well treatments are working, such as medications for arrhythmias or after a procedure like a pacemaker fitting. It鈥檚 also a useful tool to monitor patients with existing heart conditions or those at risk due to family history, lifestyle, or other health problems.
Interpreting what is an ECG test shows requires clinical judgement, but hing this information quickly can support better decision-making and early intervention when needed.
Is an ECG Test Painful? What It Feels Like During the Test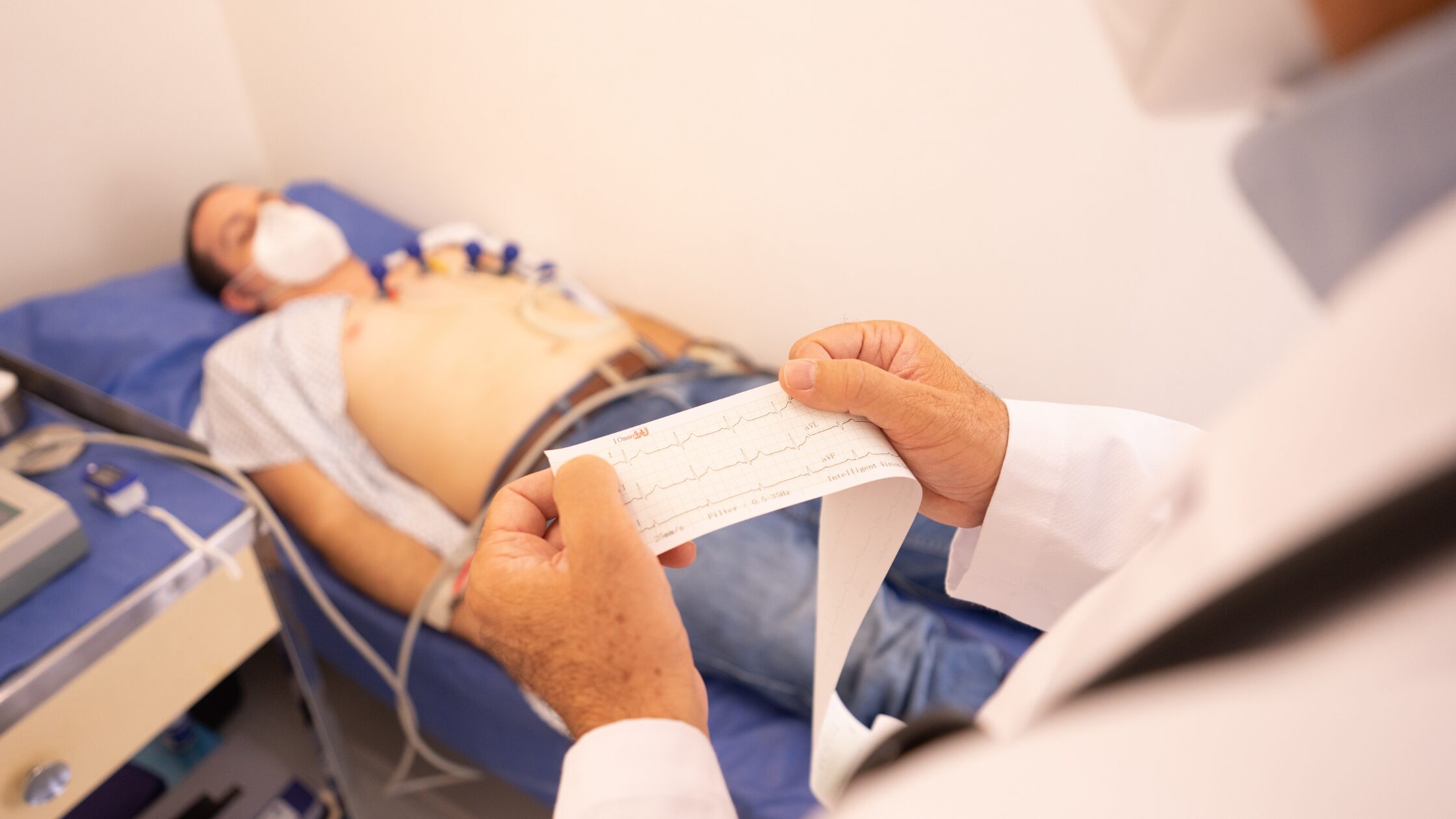
Many patients feel anxious before an ECG simply because they don鈥檛 know what to expect. As clinical professionals, it helps to reassure patients that an ECG test is entirely painless and takes only a few minutes from start to finish.
For patients who ask what is an ECG test, it can be useful to explain that it records the heart鈥檚 natural electrical activity using external sensors鈥攖here鈥檚 no discomfort, and nothing enters the body. Understanding this early on helps ease unnecessary worry.
During the test, the patient will be asked to lie flat on an examination couch. A number of electrodes, usually ten, are placed on the skin across the chest, arms, and legs. These are connected to the ECG machine via soft cables. No electricity enters the body during the test; the electrodes only record the electrical signals produced naturally by the heart.
The most patients will feel is the slight coolness of the electrode gel and, occasionally, mild discomfort when removing the sticky pads, especially if there is body hair. Movement and talking can interfere with the readings, so patients are encouraged to stay relaxed and breathe normally while the ECG is recording.
It鈥檚 also helpful to explain to patients that the ECG won鈥檛 make a noise or show instant results on a screen like in films. Instead, it quietly records data that will be reviewed either immediately or shortly after by a healthcare professional.
Putting patients at ease during an ECG is key to obtaining a clean and reliable recording. When staff are confident in describing the procedure and what it feels like, patients are more likely to relax, helping the test go smoothly and improving overall care quality.
What Is an ECG Test and How to Understand the ResultsOnce the ECG test is complete, the next step is interpreting the data. The graph produced shows wes that reflect the timing and strength of electrical signals as they pass through different parts of the heart. For clinics performing regular cardiac assessments, understanding what is an ECG test and how to apply the results effectively is essential for guiding patient care.
While many clinicians know what an ECG test is in terms of its process, it’s just as important to connect the visual output with clinical decision-making. Interpreting ECG results accurately ensures patients receive timely advice, further testing if needed, and the reassurance they often seek.
A normal ECG will show a consistent rhythm and heart rate, with we shapes that follow the standard pattern. This usually means the heart is functioning as expected, and no further immediate action is needed, though it may still be part of routine monitoring in patients with risk factors.
An abnormal ECG might reveal several things. For example:
A fast or irregular rhythm may suggest atrial fibrillation or another arrhythmia.
A delay in electrical signals could indicate heart block.
Unusual we shapes may point to reduced blood flow or signs of a past heart attack.
Large weforms could suggest enlarged heart chambers due to conditions like hypertension.
It鈥檚 important to consider ECG results alongside the patient鈥檚 symptoms, medical history, and any other investigations. In many cases, an abnormal ECG does not automatically mean something is seriously wrong, but it does act as a prompt for further assessment, whether that鈥檚 blood tests, imaging, or referral to a cardiologist.
Clinics should ensure patients understand that ECGs are just one part of the puzzle. Good communication about what the results mean, and what the next steps might be, helps build trust and ensures patients feel well supported throughout the process.
If your clinic offers cardiac testing, you may also find our beginner鈥檚 guide to diagnostic tests for heart disease useful for explaining other common assessments to patients.
When Should You Consider an ECG Test?ECG testing is a valuable tool that can be used in a wide range of clinical situations. Private clinics are often the first point of contact for patients presenting with early warning signs of cardiac problems, making access to accurate ECG interpretation essential.
You should consider offering or recommending an ECG test when a patient reports symptoms such as:
Chest pain or discomfort
Shortness of breath
Dizziness or fainting
Palpitations or a fluttering sensation in the chest
Unexplained fatigue
It鈥檚 also common to carry out an ECG in patients with known cardiovascular risk factors. This includes those with high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, a strong family history of heart disease, or those who smoke. Some clinics also use ECGs as part of routine health assessments for patients over a certain age, or prior to surgery or starting new medications.
In these situations, the ECG helps to either rule out immediate concerns or catch early signs of an abnormal rhythm or heart strain, before symptoms become more serious.
If your clinic offers ECG recording in house, hing access to professional interpretation is key. For example, many of our clients link patients to this supporting resource: How to Prepare for Your ECG Appointment for Accurate Results
With reliable reporting and quick turnaround times, clinics can improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce onward referral delays, and provide reassurance or early intervention where needed.
FAQ: Quick Answers About ECG TestsWhat is an ECG test used for?Understanding what an ECG is test begins with knowing its purpose: it鈥檚 used to check the heart鈥檚 rhythm and electrical activity. It helps detect issues like arrhythmias, signs of a previous heart attack, or other conditions that may need further investigation.
How long does an ECG test take?The test itself typically takes less than 10 minutes. Including preparation and discussion, the entire appointment usually lasts around 15 to 20 minutes.
Is an ECG test painful?No, an ECG is completely painless. Electrodes are placed on the skin to record the heart鈥檚 electrical signals鈥攏o electricity enters the body at any point.
Can patients eat or take medication before an ECG?Yes, patients can usually eat and take their medication as normal, unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional.
How soon are ECG results ailable?This depends on the clinic鈥檚 workflow and whether interpretation is handled in-house or externally. Many private clinics now partner with services like Crane Cardiac Diagnostics for fast, expert ECG analysis, often returned within 24 hours.
