 Fractions represent parts of a whole
Fractions represent parts of a whole
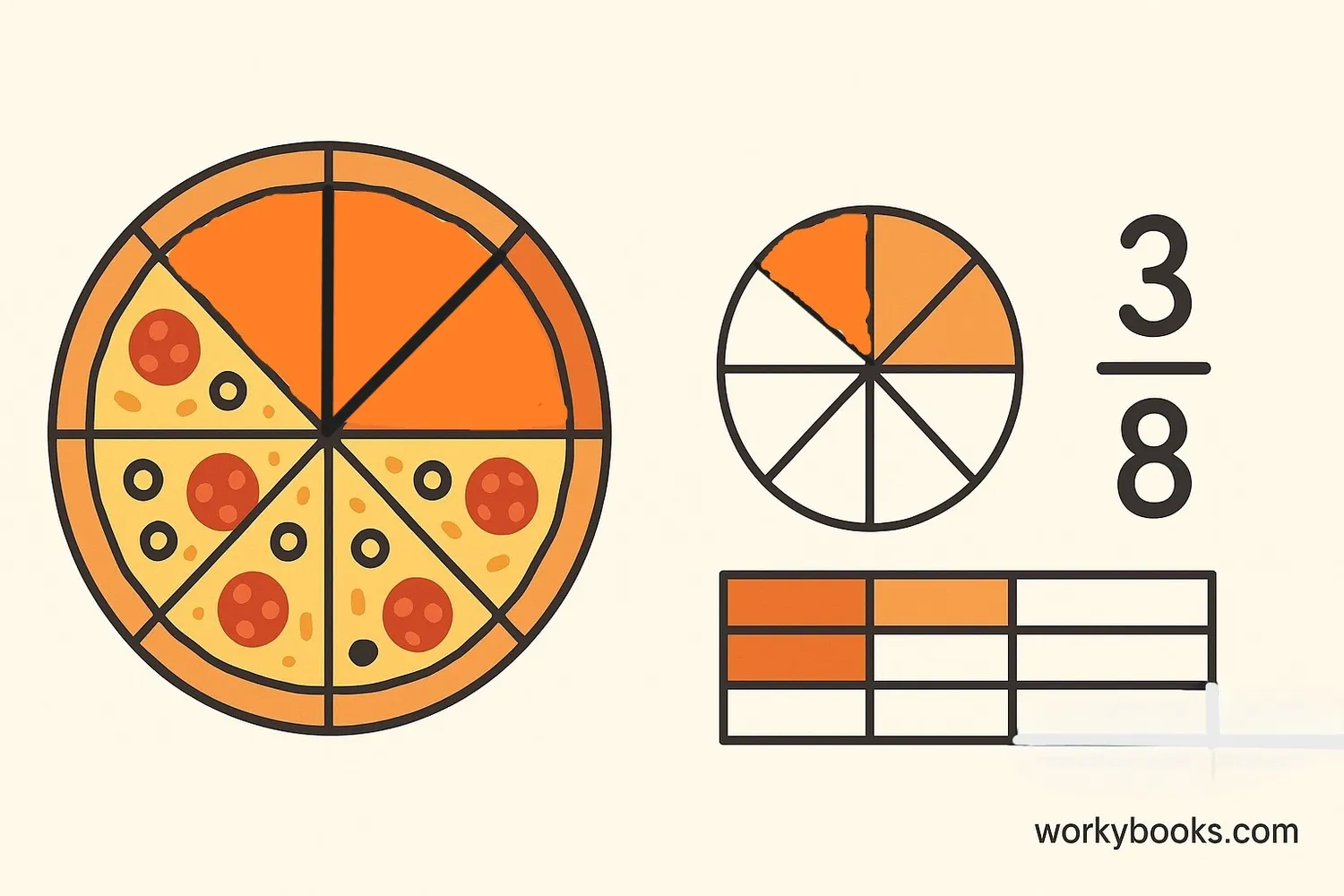
A fraction represents parts of a whole. When we divide something into equal pieces, a fraction shows how many of those pieces we he.
Fractions he two parts: - The numerator (top number) tells how many parts we he - The denominator (bottom number) tells how many equal parts the whole is divided into
For example, in the fraction ¾: - Numerator is 3 (we he 3 parts) - Denominator is 4 (the whole is divided into 4 equal parts)
Fractions must he positive integers for both numerator and denominator. The denominator can never be zero!
Key ConceptFractions represent parts of a whole and must he positive integers for both numerator and denominator.
What is a Rational Number?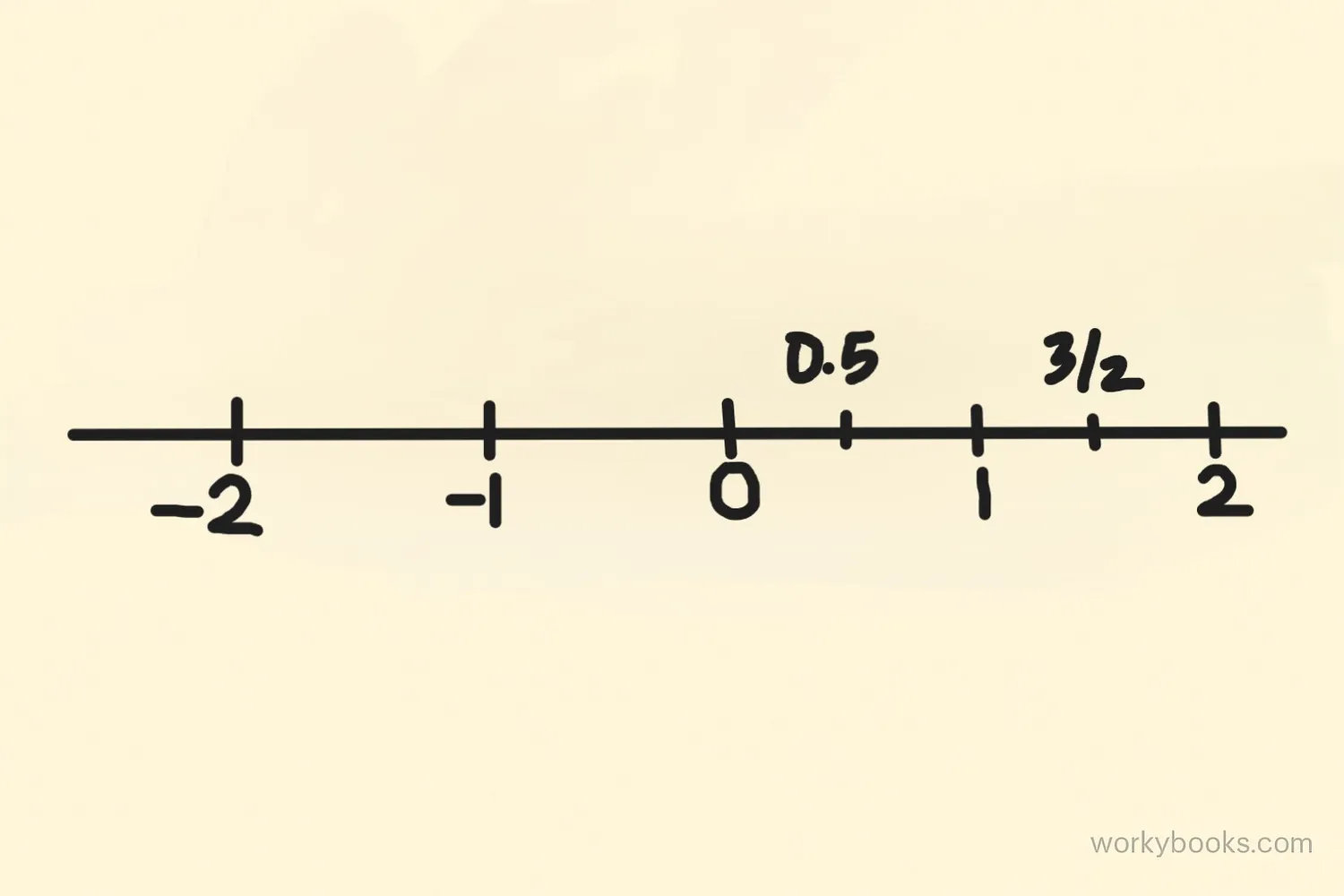 Rational numbers include fractions, integers, and decimals
Rational numbers include fractions, integers, and decimals
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not zero.
This means: - They can be written as a fraction (like 3/4) - They can be positive or negative (like -2/3) - They include whole numbers (like 5 = 5/1) - They include integers (like -3 = -3/1)
The general form of a rational number is a/b where: - a and b are integers - b is not zero
Rational Number Definition a/b where a, b ∈ ℤ and b ≠ 0Any number that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers
RememberAll fractions are rational numbers, but not all rational numbers are fractions!
Key DifferencesWhile all fractions are rational numbers, there are important differences:
Characteristic Fractions Rational Numbers DefinitionParts of a wholeRatio of two integers NumeratorPositive integerAny integer DenominatorPositive integerAny integer except zero Can be negative?NoYes Includes whole numbers?Only when denominator is 1Yes (e.g., 5 = 5/1) Includes integers?Only positive integersAll integers (positive and negative) Examples1/2, 3/4, 5/81/2, -3/4, 5, -2, 0.75 Quick TipIf you see a negative sign in a fraction, it's a rational number but not a fraction. Fractions are always positive!
Examples 3/4 Fraction and Rational Number -2/5 Rational Number (but not a fraction) 7 Rational Number (7/1) √2 Not Rational (Irrational)Let's look at some examples to understand the difference:
Example 1: 2/3 - This is both a fraction and a rational number - It has positive integers for both numerator and denominator
Example 2: -5/8 - This is a rational number because it's a ratio of integers - But it's not a fraction because fractions can't be negative
Example 3: 4 (which is 4/1) - This is a rational number (can be written as 4/1) - It's also a fraction because 4/1 has positive integers
Example 4: 0.6 (which is 3/5) - This is a rational number because it can be written as 3/5 - It's also a fraction because 3/5 has positive integers
RememberA number is rational if it can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. A fraction is specifically a ratio of two positive integers.
Practice QuizTest your understanding with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Math Master! You've shown excellent understanding of fractions and rational numbers! Good effort! Review the differences and try again. Frequently Asked QuestionsHere are answers to common questions about fractions and rational numbers:
No, fractions cannot be negative. By definition, fractions represent parts of a whole and are always positive. Negative numbers written as ratios (like -3/4) are rational numbers but not fractions. Yes, zero is a rational number because it can be expressed as a ratio of two integers (0/1, 0/2, 0/3, etc.). However, it's not considered a fraction because fractions represent parts of a whole, and zero would represent no parts. Division by zero is undefined in mathematics. If the denominator were zero, it would mean dividing something into zero parts, which doesn't make sense. For example, 3/0 has no meaning because you can't divide 3 items into zero groups. Decimals are rational numbers if they terminate (like 0.5) or repeat (like 0.333...). Decimals that neither terminate nor repeat (like π or √2) are irrational numbers. Math TriviaDiscover interesting facts about numbers and mathematics:
Ancient FractionsThe ancient Egyptians used fractions as early as 1800 BC. They had special symbols for fractions like 1/2, 1/3, and 1/4, and represented other fractions as sums of these unit fractions.
Rational Numbers in NatureMany patterns in nature follow rational numbers. The Fibonacci sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13...) creates ratios that approach the golden ratio, which is an irrational number approximately equal to 1.618.
Rational Numbers in SpaceAstronomers use rational numbers to calculate distances between planets. For example, the ratio of Earth's distance from the Sun to Mars' distance is about 1.5, which is the rational number 3/2.
Largest DenominatorThe fraction with the largest denominator commonly used in mathematics is the "googolplex," which is 1 followed by a googol of zeros. A googol is 10100 - that's 1 followed by 100 zeros!
